In the world of finance, the S&P rate is a term that often comes up in discussions about market trends and investment strategies. But what exactly is the S&P rate, and why is it so crucial for investors and financial analysts? This article delves into the details of the S&P rate, its significance, and how it can impact your investment decisions.
What is the S&P Rate?
The S&P rate, also known as the S&P 500 Index, is a stock market index that tracks the performance of 500 large companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States. It is one of the most widely followed indices in the world and serves as a benchmark for the overall health of the U.S. stock market.
The Importance of the S&P Rate
Understanding the S&P rate is essential for several reasons:
Market Performance Indicator: The S&P rate provides a snapshot of the overall performance of the U.S. stock market. By tracking the performance of 500 large companies, it offers a comprehensive view of market trends and economic conditions.
Investment Strategy: Investors often use the S&P rate as a guide for their investment strategies. For example, if the S&P rate is rising, it may indicate a strong market and a good time to invest. Conversely, a falling S&P rate may suggest a bearish market and a cautious approach.
Economic Indicator: The S&P rate is also considered an economic indicator. It reflects the overall economic health of the country and can provide insights into future economic trends.
How the S&P Rate is Calculated
The S&P rate is calculated using a complex formula that takes into account the market capitalization of each company in the index. The market capitalization is the total value of a company's outstanding shares and is calculated by multiplying the number of shares by the current market price.
Impact of the S&P Rate on Investment Decisions
The S&P rate can have a significant impact on investment decisions. Here are a few examples:
Asset Allocation: Investors often allocate their assets based on the S&P rate. For instance, if the S&P rate is rising, they may allocate more of their portfolio to stocks. Conversely, if the S&P rate is falling, they may shift towards bonds or other fixed-income investments.
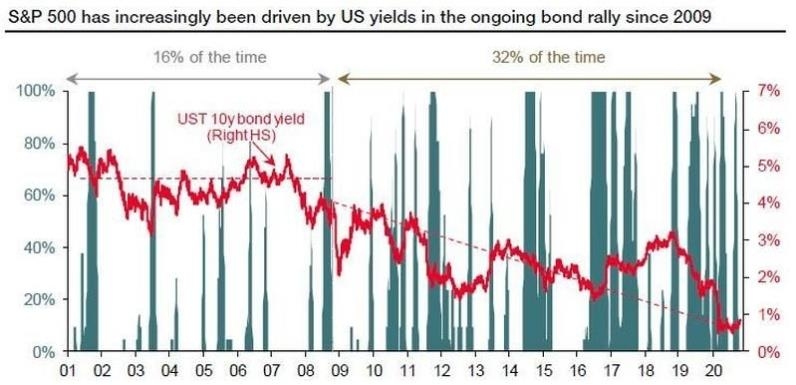
Risk Management: The S&P rate can help investors manage their risk. By monitoring the S&P rate, they can adjust their portfolio to align with their risk tolerance.
Market Timing: Some investors use the S&P rate to time the market. They may enter or exit the market based on the direction of the S&P rate.
Case Study: The S&P Rate During the 2008 Financial Crisis
One notable example of the impact of the S&P rate is during the 2008 financial crisis. The S&P rate plummeted by nearly 50% from its peak in October 2007 to its trough in March 2009. This dramatic decline reflected the severe economic downturn and the resulting impact on the stock market.
Investors who were able to recognize the downward trend and adjust their portfolios accordingly were able to mitigate their losses. Conversely, those who ignored the warning signs and continued to invest heavily in the stock market during this period suffered significant losses.
Conclusion
The S&P rate is a crucial tool for investors and financial analysts. By understanding its significance and impact, investors can make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of the stock market. Whether you are a seasoned investor or just starting out, familiarizing yourself with the S&P rate is essential for success in the financial world.